SEO Glossary of Terms

Common SEO Terminology For Beginners
A clear understanding of terms is vital in any field of study or expertise. We have created this SEO glossary with the beginner in mind and with the hope that it will provide you with an essential resource to which you can return repeatedly.
Whether you are a newcomer seeking foundational knowledge or a seasoned professional looking to update your terminology, this seo glossary offers clarity and context for the concepts discussed throughout this site.
The terms included in this SEO glossary have been carefully selected to reflect our field’s most relevant and commonly used words. Each entry is designed to enhance your comprehension, bridge gaps in understanding, and facilitate effective dialogue among peers.
We encourage you to refer to this SEO glossary frequently, as it will serve as a supportive tool for navigating the sometimes murky world of the Internet.
SEO Glossary of Terms - Part I
A
Add-on/Plug-in:
A software product designed to enhance the functionality of another software product, commonly seen with platforms like WordPress.
Adware:
Software that delivers advertisements to users, often tracking their visits to specific websites. It may be bundled with purchased software or included in free downloads.
Algorithm (of a search engine):
An aspect of a search engine that determines which indexed pages appear in search results and their order. The workings of Google’s algorithm are confidential, and the factors influencing this order change regularly.
AlsoAsked.com:
A tool designed to generate keywords. It enables users to discover frequently asked questions about a specific topic or keyword by collecting, organizing, and displaying the “People Also Ask” questions in Google’s search results.
Answer box (in Google):
An element of search results that appears among organic links. Answer boxes provide suggestions for questions related to your search query.
Archive Page:
Archive pages are automatically generated when you create a category, tag, or other taxonomy in WordPress. Posts or product pages that belong to that taxonomy are displayed in a list on these archive pages.
B
Bounce rate:
A metric that measures the percentage of visitors who land on your website without engaging with the page. This includes not clicking on menu items, ‘read more’ links, or any internal links. A user is considered to have bounced if there is no interaction with the landing page, resulting in a single-page visit. Bounce rate can indicate the quality of a webpage and the engagement level of your audience.
Breadcrumbs:
Unlike Hansel and Gretels famous story, a breadcrumb trail is a small text path often located at the top of a page. For example, on Tweakmysite.com, the path to our glossary page is in the top left corner – Home » SEO Glossary of Terms.
Browser:
A software program that enables users to search for and view information on the Web. Examples include Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Yahoo!, Bing, and Firefox.
C Caching:
The process of saving local copies of downloaded content to minimize repeated downloads. Sensitive pages should prohibit caching to safeguard privacy.
Cannibalization (of your content):
If you have multiple articles that are very similar and optimized for the same keyword, you’ll end up competing with your own content. This can result in lower rankings on Google for all of these articles.
Canonical Link:
A canonical link element informs search engines which version of a collection of similar or identical pages you want Google to include in search results.
Categories:
Categories allow for broad groupings of posts or page topics. They can be organized hierarchically, allowing for subcategories. Each post must be assigned to at least one category. For instance, a blog might have a category for Books, with subcategories like Documentaries, Novels, or Sci-fi.
Classifying Link:
A classifying link helps Google and users understand your site’s structure. Examples of classifying links include links to your categories, breadcrumbs, and site-wide menus.
Cloud:
Services and software that operate on the Internet rather than on a local computer. Examples include Apple iCloud, Dropbox, Netflix, Amazon Cloud Drive, Flickr, Google Drive, and Microsoft Office 365.
Commercial intent:
This refers to when people wish to purchase something soon and conduct research before deciding.
Contextual Link:
A contextual or internal link helps Google and users identify essential pages within your site. These links are embedded in your content and refer to other pages on your site.
Conversion:
A conversion occurs each time a visitor completes a desired action on your website, such as clicking through to another page, subscribing to a newsletter, or purchasing a product.
Cookie:
A web server can retrieve a small text file stored on a client machine later, allowing the server to track user activities and maintain session integrity.
Copywriting:
The practice of writing text specifically for advertising and other marketing purposes.
Cornerstone content:
Cornerstone content consists of the articles on your website that you take the most pride in. They reflect your business, communicate your mission, and are well-written. These are the articles you’d like to rank highly in search engines. Cornerstone articles are typically comprehensive; they synthesize insights from various blog posts.
Crawlability:
This refers to how easily Google can crawl your site. Crawlers may be blocked from accessing your website through several methods, including the robots.txt file, HTTP headers, or robots meta tags. If a website or a specific page is blocked, it signals to Google’s crawler not to visit. As a result, the site or page is unlikely to appear in search results.
Crawler (also: spider, bot, robot):
An element of a search engine that continuously browses the internet, following links from one web page to another while storing the HTML versions of all pages in a massive database known as the index. Pages stored in the index may show up in search results.
D De-listing:
When a web page or pages are removed from a search engine directory, it can be temporary or permanent and can happen for any number of reasons, including a penalty from the search engine, a change in search engine crawl priorities, or a change in the page’s location.
Domain name:
The customizable or branded part of a website’s name. For example, http://www.yoursite.com
E E-commerce:
A specific type of website that sells products physical or digital products online. Short for “Electronic Commerce.”
Everflux:
Google’s nickname for the continuous change in search engine algorithms and indexes.
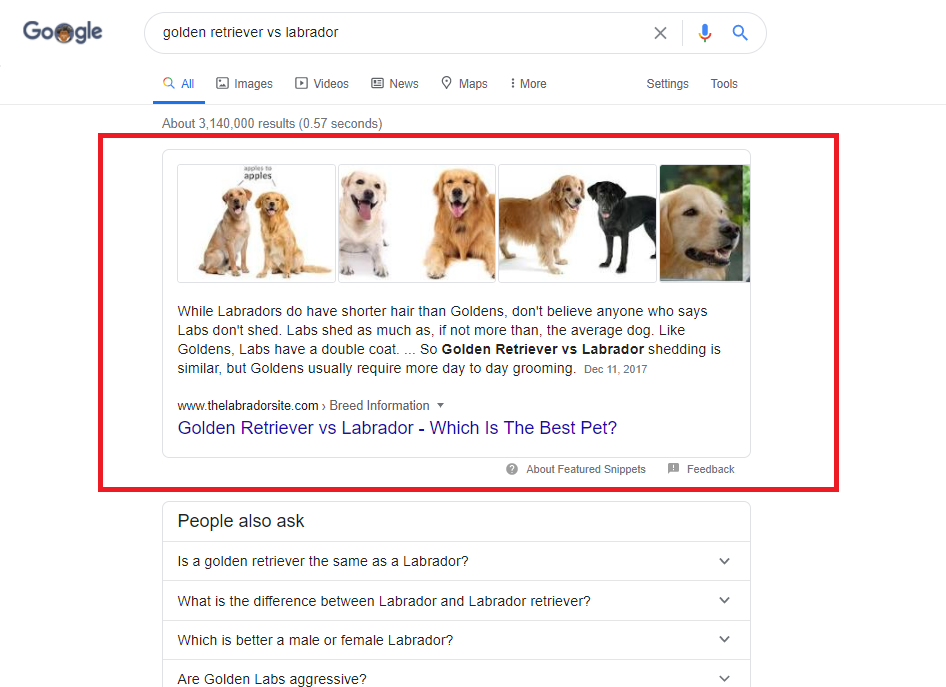
F Featured Results (in Google):
Featured results are highlighted search boxes that provide answers to queries typed in the Google search bar. These results often appear as a paragraph or bulleted list, sometimes accompanied by an image, and are positioned above the regular organic search results.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP):
The standard method for downloading and uploading files over the Internet. With FTP, you can log in to a server and transfer files, allowing you to either send or receive files.
Firewall:
A hardware or software-based network security system manages incoming and outgoing traffic according to specified security rules.
G
Google:
The world’s most popular search engine. Google’s Mission is to “organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.”
Googol:
Ten to the 100th power, or 1 followed by 100 zeros. Googol almost became Google’s name. If it wasn’t for a typo, it may never have happened.
Googolplex:
Ten raised to the power of a Googol, or 1, followed by a googol of zeros.
Google Ads:
An online advertising service created by Google that allows advertisers to pay for displaying brief ads in the Google ad network to web users.
Google Ads Keyword Planner:
A keyword research tool within Google Ads that helps you find the most relevant keywords.
Google Analytics:
A web analytics service provided by Google that tracks and reports website traffic.
Google Search Console:
A web service from Google for webmasters that allows them to check their site’s indexability and enhance their websites’ visibility.
Google Trends:
A Google tool that compares the search frequency of different terms.
H
Head keyword:
The most important keywords that form the basis of your keyword research sheet and strategy. After identifying your head keywords, you can create longer tail keywords. Note: head keywords can contain multiple words.
Holistic (Organic) SEO approach:
An SEO strategy that focuses on enhancing every aspect of your site to improve its ranking in search results. Google aims to create the perfect search engine that helps users find the best results for their queries.
Homepage:
The first page displayed when a web browser starts. It is also the main, or front page of a website. It provides an introduction or content along with links to other pages.
(HTTP) Hypertext Transfer Protocol:
Hypertext Transfer Protocol is the abbreviation for the set of rules that governs how web pages are transferred across the Internet.
HTTP Status Error Codes:
200: OK / Success:
The 200 status code indicates success. This means that when a client requests content, the server responds with a 200 success message along with the requested content. This scenario pleases both the server and the client, as well as the visitor. Any status codes in the 2xx range signify some level of success.
301: Moved Permanently:
A 301 HTTP header is used when the requested URL has been permanently moved to a new location. As you work on your site, you will frequently implement 301 redirects to direct old URLs to new ones. If you fail to do this, users attempting to access the old URL will encounter a 404 error page—something you want to avoid. A 301 redirect ensures that the link authority of the old URL transfers to the new URL.
302: Found:
A 302 code indicates that the requested destination has been located but resides in a different location. However, this status code could be clearer as it doesn’t clarify whether the situation is temporary. Use a 302 redirect only if you want to temporarily redirect a URL to another source, knowing that you’ll eventually use the original URL again. Since search engines understand that the original URL will be used again, none of the link value transfers to the new URL. Therefore, avoid using a 302 for significant changes in site structure or when moving your domain. Additionally, prolonged 302 redirects may lead search engines to treat them as 301 redirects and no one wants that.
304: Not Modified:
A 304 status code indicates that the requested resource has stayed the same since the last time the client accessed it. This means the server doesn’t need to resend the resource but instructs the client to use a cached version instead. The 304 response helps save crawl budget for large websites since Google’s crawler will not revisit unchanged pages, allowing it to focus on new and updated content.
307: Temporary Redirect:
The 307 status code replaces the 302 in HTTP/1.1 and is a temporary redirect. You can use a 307 redirect when temporarily redirecting a URL to a new location while keeping the original request method intact. A 307 works similarly to a 302, but it indicates that the URL has a temporary new location. The request can change over time, so clients must continue using the original URL for new requests.
403: Forbidden:
A 403 error informs the browser that the requested content is forbidden for the user. If a user lacks the correct login credentials, this content will remain inaccessible to them.
404: Not Found:
The 404 HTTP status code is one of the most visible—and significant—status codes. When a server returns a 404 error, it indicates that the content was not found and may have been deleted. To avoid frustrating visitors with these messages, fix these errors when possible. Use a redirect to guide visitors from the old URL to a new article or page with related content.
410: Gone Forever:
The 410 status code indicates the same result as a 404, signaling that the content is not found. However, a 410 informs search engines that the requested content has been deleted. This makes it more precise than a 404, instructing search engines to remove the URL from their index. Before permanently deleting a page from your site, consider whether an equivalent page exists elsewhere. If so, create a redirect; if not, you should improve it instead of deleting it.
451: Unavailable for Legal Reasons:
The 451 HTTP status code indicates that the requested content has been removed for legal reasons. If you received a takedown request or were ordered by a judge to take specific content offline, use this code to inform search engines about the page’s status.
500: Internal Server Error:
A 500 error is a general message indicating that the server encountered an unexpected condition that prevented it from fulfilling the request. These errors can originate from various sources, including issues with your web host or malfunctioning scripts on your site. Check your server logs to identify the problem.
503: Service Unavailable:
A 503 status code is a server-side error indicating that the server can temporarily not handle the request. This may be due to overloading, maintenance, or other server-related issues. A prolonged 503 status can negatively affect SEO, as it may signal to search engines that the site is unreliable. To mitigate negative impacts, a 503 status should be reserved for brief situations and provide crawlers with clear information about when the site will be back online. You can use the Retry-After value to suggest that crawlers try again after a specified period.
Hummingbird update:
A Google update that set the foundation for voice search, paying close attention to each word in a query and considering the entire phrase rather than just individual words. The Hummingbird update was released in 2013.
I
Incognito mode:
Incognito mode is a privacy feature in some web browsers that disables browsing history and web cache. Searching in incognito mode prevents search engines from considering previous searches when displaying results.
Index:
An aspect of a search engine is a vast database where the HTML versions of pages discovered by the crawler are stored. Pages saved in the index could appear in search results based on how the search engine’s algorithm evaluates them.
Indexability:
The ability of a search engine to include a page in its index.
Informational intent:
People have informational intent when they seek information on a specific subject. For example, Tweakmysite.com creates blog posts for users looking for SEO information.
Internal link:
Internal links (contextual links) are web page links that direct to another page or resource (e.g., an image or document) within the same website or domain. They connect your content and provide Google with insights into your site’s structure, helping to establish hierarchy and assign more link value to essential pages.
Internet Protocol (IP) Address:
The Internet consists of local, regional, national, and global computer networks. Each computer connected to the Internet is identified by a unique set of numbers known as an Internet Protocol (IP) address. An IP address consists of four numbers separated by periods, such as 123.456.789.01
SEO Glossary of Terms - Part II - J - R
J JSON-LD:
JSON-LD is a markup language used with Schema.org. Markup is a way to write code. Alongside JSON-LD, you’ll find other markups like Microdata and RDFa on Schema.org.
K
Keyword:
A word or phrase that you want your website to rank for so that when individuals search for that term in a search engine, your site appears.
Keyword research:
The process of creating an extensive list of keywords you aim to rank for.
Keyword stuffing:
The practice of filling pages with excessive (and often unrelated) keywords or numbers to manipulate search engine ranking.
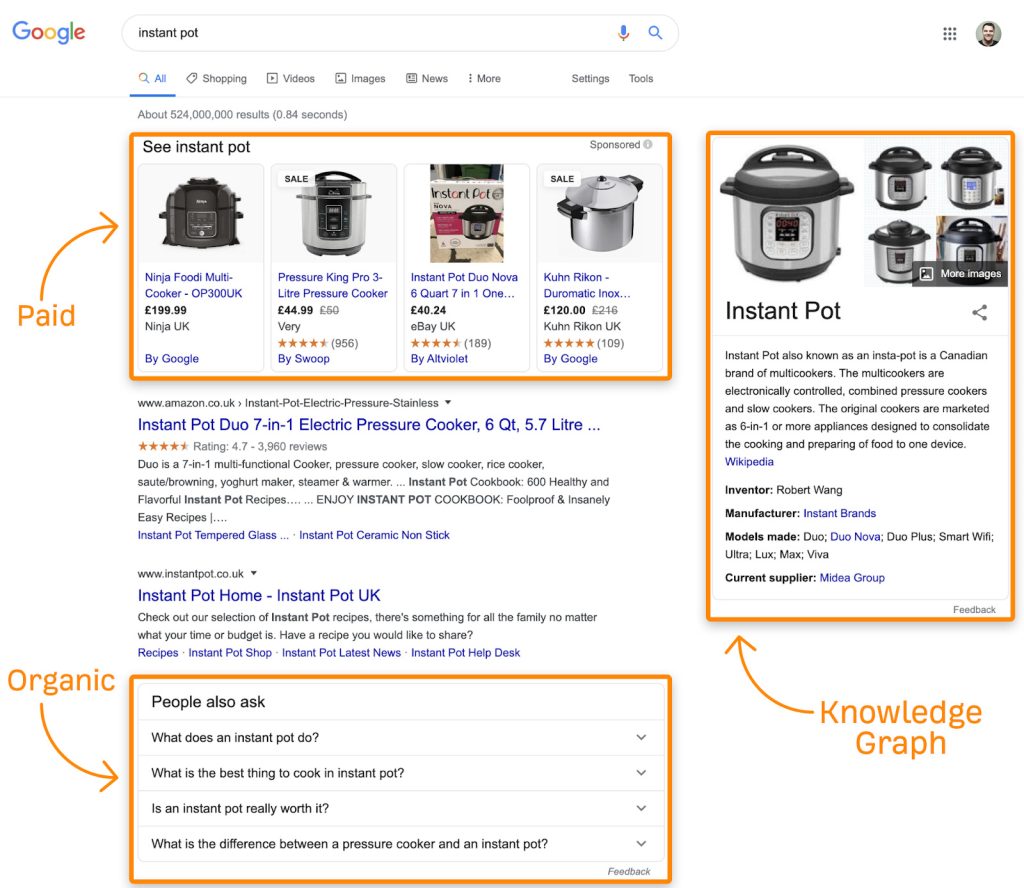
Knowledge Graph Card:
A Knowledge Graph Card is a block typically found on the right side of the search results page. It contains relevant context-specific information related to your search, such as details about a company or a person.
L
Landing pages:
The pages you aim for your audience to reach while searching for a particular keyword. Landing pages also occur as a sales page or in a sales funnel.
Link building:
There are two types of link building: white-hat and black-hat. White-hat link building involves fostering an engaged community and promoting your website to relevant audiences, whereas black-hat strategies may include buying links, which can involve paying for links or sending free products in exchange for a link. Black-hat strategies almost always result in lower rankings and ultimate failure.
Long tail keyword:
These are more specific and less common keywords compared to mid-tail keywords. They usually cater to a niche audience. The longer and more specific the search terms are, the easier they tend to be to rank for. The length of long-tail keywords is relative; they may consist of three or four words for larger companies and six or more words for smaller ones.
M Malware:
Malicious software designed to damage, disrupt, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems. A computer virus is a type of malware that can replicate within a user’s computer.
Mid-tail keyword:
The head keyword is derived from more specific and longer keywords. The length of mid-tail keywords varies – they may be concise for large companies and more extensive for smaller businesses.
Mission:
A brief statement that outlines a company’s purpose, target markets, and competitive advantages; it summarizes your business goals and philosophies.
Mobilegeddon update:
A Google update that prioritizes sites with mobile-friendly pages in mobile search results. The Mobilegeddon update was introduced in 2015.
Mobile Indexing First index:
A new indexing system Google began transitioning to in 2018. This update means Google will rank sites based on the quality of their mobile version instead of the desktop version.
N
Navigational intent:
Users exhibit navigational intent when they search for a specific website by entering its name in a search engine. For instance, if someone searches for “Wordpress SEO,” they are likely attempting to access our website, Tweakmysite.com.
Niche:
Merriam-Webster defines a niche as a smaller market segment with specific needs, which is “the situation in which a business’s products or services can succeed by being sold to a particular group of people.”– ‘Train fans is an example of a niche, but if you drill down one more level, you will find ‘Train spotters’, a much more dedicated and motivated group for your target niche.
Nofollow Tag:
A nofollow tag is a robot meta tag instructs search engine robots not to follow any links on the page.
Noindex Tag:
A no-index tag is a robot meta tag that prevents search engines from displaying the page in their results.
O Organic search results:
The unpaid search results in which we all strive for a top position. Google’s search engine results page (SERP) displays seven to ten organic links that best match your search parameters.
Orphaned Content:
Orphaned content refers to material that lacks direct links, leaving it floating around the www. It is destined to live a lonely and undiscovered life. Unknown by visitors or search engines—a very sad state of affairs. (sniff).
P Page:
A page is a document on the World Wide Web identified by a unique URL.
Page swapping:
A tactic for ranking a specific page, then replacing it with another once it has achieved a good position in search results.
Paid search results:
The paid search listings displayed above organic (unpaid) links. These links are ads for which advertisers have paid Google to place them at the top of search results for specific terms and are labeled ‘Sponsored’.
Panda update:
A Google update aimed at reducing the ranking of websites created solely to manipulate search engine results. The first Panda update was launched in 2011 and has been re-run periodically.
Passive Voice:
Passive voice is a grammatical construction in which the sentence’s subject is acted upon instead of acted upon. It’s best to avoid using passive voice in your articles, as text heavy with passive voice can be difficult and unattractive to read.
Penguin update:
Penguin is a Google update that evaluates the quality of incoming links to websites. If the links are deemed artificial (such as those obtained by purchasing or exchanging links), Google no longer gives them link value. The first Penguin update was rolled out in 2012 and has been executed multiple times; it is now known to run continuously.
Phishing:
The term comes from E-mails or communications crafted to deceive you into providing sensitive information, such as passwords or account numbers.
Possum update:
A 2016 Google update affected search results based on the user’s physical location and the specific wording of the query.
Q Query:
The words or phrases you enter into a search box. The algorithm then accesses the index and returns the results to you in SERP’s
R
RankBrain:
A Google algorithm and machine learning system that helps Google better understand query meanings and provides the most relevant search results. RankBrain includes both query processing and ranking components.
Ranking:
Securing a high position for your website in a search engine’s results, such as those provided by Google. The algorithm of a search engine determines your site’s ranking.
Redirection (of URLs):
Redirection is a technique that allows a web page to be accessible under more than one URL address. When a web browser attempts to open a redirected URL, it automatically leads to a different page with another URL.
Rich Card:
Rich Cards are an extension of rich snippets. On mobile devices, a card serves as the introductory presentation unit of a search result. Like rich snippets, rich cards include extra information, such as aggregate ratings, prices, or availability, offering a well-structured presentation that is easy to understand and act upon.
Rich Snippet:
A type of search result that presents more information than just the title, URL, and meta description; it may include an image, a rating, and stock availability for a product. Rich snippets stand out from standard snippets, resulting in higher click-through rates.
Robots Meta Tag:
A robots meta tag specifies how a particular page should be indexed and displayed in search results. It is placed in the <head> section of a web page.
Robots.txt File:
A robots.txt file instructs search engines which areas of your website they can or cannot access. Search engine crawlers, also known as robots, read this file.
SEO Glossary of Terms - Part III - S-Z
S Schema.org:
Schema.org is a project developed by major search engines to provide structured data markup that they support. You can use schema.org to find the appropriate markup for your page.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO):
Optimizing websites to achieve a high position in Google’s (or another search engine’s) organic search results.
Search Engine Results Page (SERP):
The page the search engine displays shows the (organic and paid) search results most relevant to your query.
Search Intent:
Search intent refers to the underlying purpose of a user’s query in a search engine. It reflects what people hope to find and expect when they enter their search terms. There are four types of search intent: informational intent, navigational intent, commercial intent, and transactional intent.
Server Log:
Data servers automatically record information when a website is accessed. This information usually contains the user’s web request, IP address, browser type, language, date and time, and session cookies.
SEO Glossary: What you are reading now.
Site Structure:
Site structure involves organizing and classifying your content and adding links to create context within your site.
Snippet:
The user is shown a search result, which consists of an SEO title (in blue), a slug (in green), and a meta description (in black).
Spyware:
Software that collects personal information from users without consent, sometimes taking control of the user’s computer covertly.
Syndicated Content:
The practice of distributing content across third-party websites, which may include full articles, snippets, links, or thumbnails.
T Tags:
Tags allow for the grouping of posts or pages. While similar to categories, tags are typically used to provide more detailed descriptions of your posts. Tags are independent and do not have a hierarchical relationship, making their use optional.
Taxonomies:
WordPress employs taxonomies to group content. Taxonomy refers to a collection of items (in this case, website pages) that share common characteristics. This organization helps your visitors find related articles more easily. The default taxonomies in WordPress are categories and tags.
TLS/SSL:
Cryptographic protocols (Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)) ensure secure communications over a network.
Traffic potential:
A score that estimates the popularity of a particular search term on Google. Traffic potential is rated on a scale from 1 to 10, where 1 indicates infrequent searches and 10 denotes high search activity.
Transactional intent:
This occurs when individuals look to purchase after conducting earlier research with commercial intent. For example, our sales pages at Tweakmysite.com include several buttons allowing users to make a purchase.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP):
A set of codes that allows two devices to establish a connection and exchange data efficiently.
Trojan Horse:
A type of malware that pretends to be legitimate software while carrying out harmful actions.
U
Universal search:
Google uses this method to deliver search results, providing links to websites that best match the search parameters and digital content, including news articles, images, and videos.
Unique selling points (USPs):
The features that differentiate your business from competitors allow it to stand out in the marketplace.
URL – Uniform Resource Locator:
A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is a unique identifier used to locate a resource on the Internet, often called a web address. URLs contain several components—such as a protocol and domain name—that guide a web browser on how and where to access a resource.
User experience (UX):
UX is a person’s overall experience when using a product, such as a website, app, or mobile phone, specifically regarding its ease of use and overall enjoyment. It considers how a product makes users feel: Does it excite or satisfy them? Is it enjoyable to use? Can it help them achieve their goals effortlessly? UX is crucial for SEO, as search engines strive to deliver the best results for users.
V
Virtual private network (VPN):
A technology that establishes a secure and encrypted connection over a less secure network, such as the Internet.
Virus:
A computer code capable of self-replication is often designed to damage systems or files, corrupting data.
Voice search:
A search method that allows users to conduct searches on the internet using voice commands.
W
Web (as in www World Wide Web):
Similar to a spider web, the www is a system of internet servers that hosts specially formatted documents in HTML (HyperText Markup Language). The HTML code contains links to other documents and multimedia files.
Worm:
A self-replicating program that spreads across computer networks and often performs harmful actions without user intervention.
WYSIWYG:
It is an acronym that stands for “what you see is what you get.” WYSIWYG editors (drag-and-drop) allow web designers to adjust the content and layout of a given webpage directly without needing to enter any commands or upload FTP files.
X XML Sitemap:
An XML sitemap is a file that lists all important pages of a website. This ensures search engines like Google, Bing, and others can find and crawl them. It acts like a roadmap for search engines, highlighting the structure of your site and providing the data they need to make your pages visible in search results.
Y Yandex:
Yandex is the most prominent Search Engine in Russia and one of the largest in the world. It was founded in 1997 by Arkady Volozh and Ilya Segalovich and has grown continuously. The company offers various Internet services such as search engines, e-mail services, maps, etc.
Z Zoogle:
A zoogle is not a standard mathematical term like googol or googolplex and have any definition in mathematics. It is used more as a humorous, a joke word number even larger than a googolplex.
Thank you for reading our seo glossary. We hope you found it more interesting than counting sheep.








